Overview
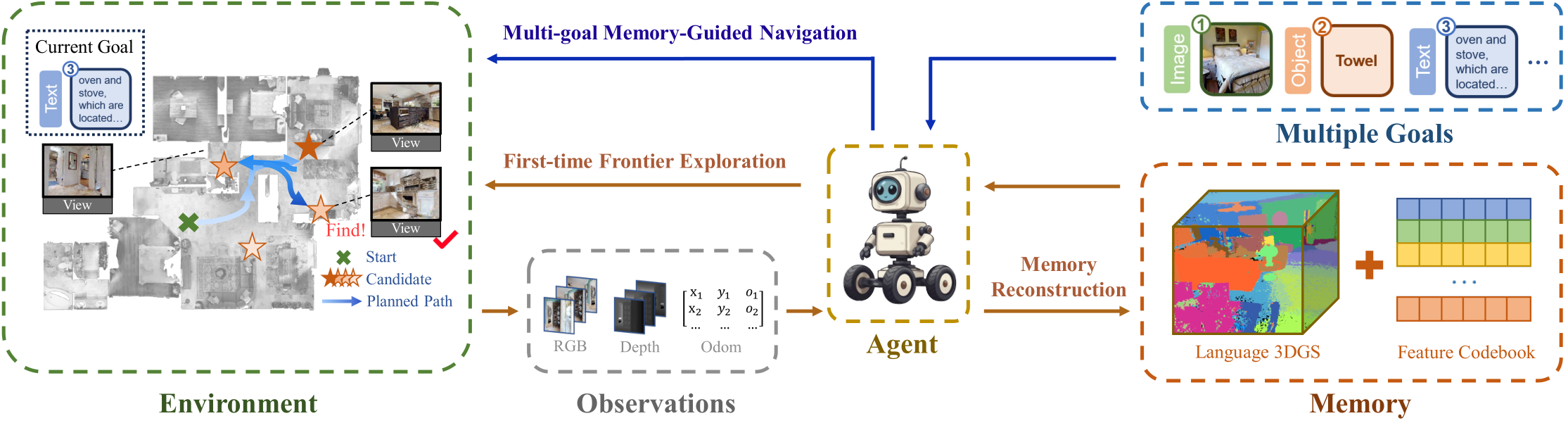

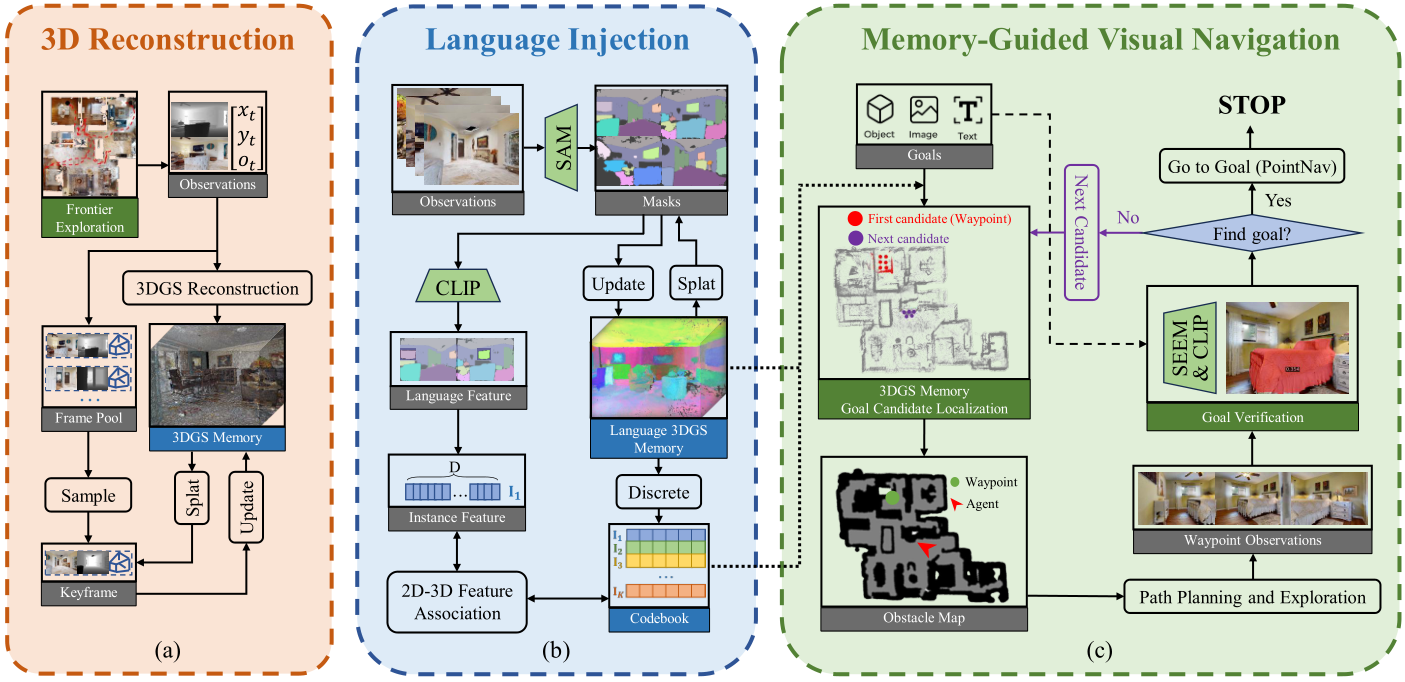
Language 3DGS Memory Reconstruction and Memory-Guided Visual Navigation Pipeline
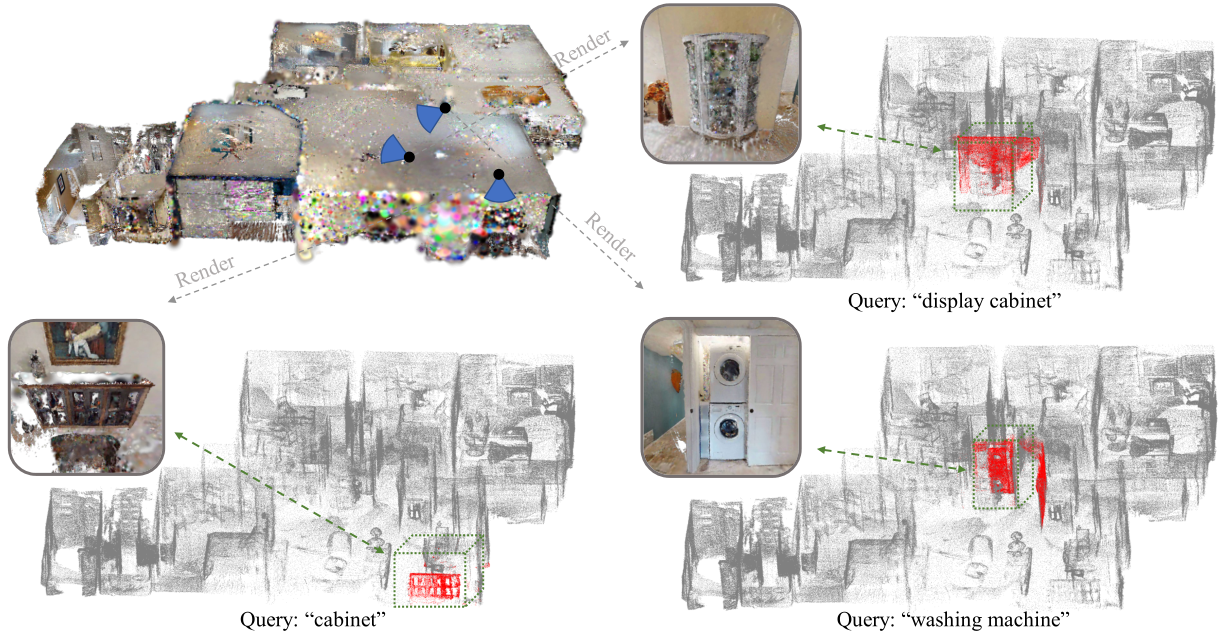
Instance Query Illustration: Different query texts are input, and corresponding responses are retrieved from the 3DGS. The rendered results from corresponding viewpoints show that the queries match the expected outcomes.
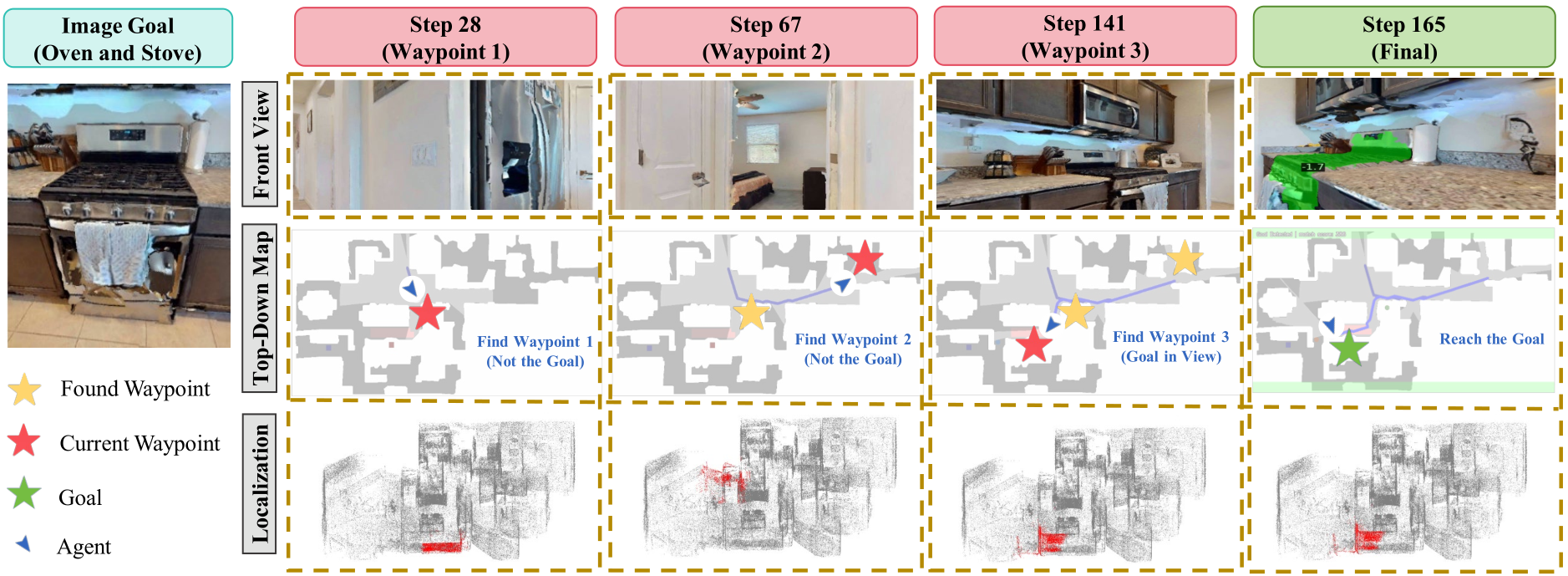
Step-by-step Visualization of Memory-Guided Navigation to an Image Goal: Columns show key steps (28, 67, 141, 165), rows show the front view, the top-down map, and the 3D localization results (red). In this case, the agent reaches waypoint-1/2/3 (yellow star; current waypoint in red). After checking the first two, it arrives at the third where the goal verification module identifies the goal. Then the agent proceeds to the final goal (green star) and the subtask successfully terminates at step 165.